
In a world that is becoming increasingly conscious of its environmental impact, sustainability has become more than just a buzzword. From energy-efficient buildings to eco-friendly practices, the global community is embracing a greener future. One of the cornerstones of this movement is LEED certification. What is LEED certification? What benefits does it bring to people, businesses, and the environment?
Whether you’re a building professional, an environmental enthusiast, or simply curious about the green building revolution, understanding LEED certification is essential.
What is LEED certification?
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design or commonly known as LEED, is a certification program that promotes sustainable practices in the design and development of built environments. LEED’s development grew from the formation of the US Green Building Council (USGBC) in 1993 by three individuals: David Gottfried, Mike Italiano and Rick Fedrizzi, who served as president, CEO and founding chair of the organization.
What is the US Green Building Council (USGBC)?
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) is a non profit organization that expresses its commitment to creating a sustainable future through cost- and energy-efficient green buildings. USGBC exists with a mission to transform the way built environments and communities are designed, established, and operated, enabling a prosperous, an environmentally and socially responsible environment that improves the quality of life.
The role of USGBC
Development of LEED Standards
- The USGBC developed and continues to update the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) rating system. From the year 1998’s v1.0, LEED continuously evolves and is currently offered as LEED v4.1
Advocacy for Sustainable Policies:
- The USGBC works with government officials, policymakers, and industry stakeholders to promote energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and green building practices.
Educational Resources
- The USGBC offers a range of educational programs, workshops, and resources to educate professionals and the general public about green building practices, sustainable design strategies, and LEED certification.
LEED rating systems
LEED offers various rating systems to accommodate different types of buildings and projects. Each rating system focuses on specific aspects of sustainability and provides a framework for evaluating and certifying the environmental performance of a building or community.
Building Design and Construction (BD+C)
This rating system is for buildings that are new construction or major renovations. It encompasses a wide range of project types, including
- New Construction and Major Renovation. New construction or major renovation of buildings that do not primarily serve residential, K–12 educational, retail, data centers, warehouses and distribution centers, hospitality or health care uses.
- Core and Shell Development. Buildings that are newly constructed or renovated for the exterior shell and core mechanical, electrical, and plumbing units, but not a complete interior fit-out.
- Schools. Buildings made up of core and ancillary learning spaces on K–12 school grounds. LEED BD+C: Schools may be used for higher education and nonacademic buildings on school campuses.
- Retail. Buildings used to conduct the retail sale of consumer product goods. Includes both direct customer service areas (showroom) and preparation or storage areas that support customer service.
- Data Centers. Buildings specifically designed to meet the needs of high-density computing equipment . LEED BD+C: Data Centers only address whole-building data centers (greater than 60%).
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers. Buildings used to store goods, manufactured products, merchandise, raw materials or personal belongings, such as self-storage.
- Hospitality. Hotels, motels, inns or other businesses within the service industry that provide transitional or short-term lodging, with or without food.
- Healthcare. Hospitals that operate 24 hours a day, seven days a week and provide inpatient medical treatment, including acute and long-term care.
LEED for Interior Design and Construction (ID+C)
This rating system is for complete interior fit-out projects. This includes applications for Commercial Interiors, Retail ,and Hospitality.
- Commercial interiors. Interior spaces aside from retail or hospitality.
- Retail. Interior spaces used to conduct the retail sale of consumer product goods.
- Hospitality. Interior spaces of hotels, motels, inns or other businesses within the service industry that provide transitional or short-term lodging, with or without food.
Building Operations and Maintenance (O+M)
This is for spaces that may be undergoing improvement work or little to no construction. Take note that a project must be fully operational and occupied for at least one year.
- Existing Buildings. Existing whole buildings.
- Existing Interiors. Existing interior spaces that are contained within a portion of an existing building. Interior spaces may serve commercial, retail or hospitality purposes.
Neighborhood Development (ND)
This is offered to new land development projects or redevelopment projects containing residential uses, nonresidential uses, or both.
- LEED ND: Plan. Projects in conceptual planning or master planning phases, or under construction.
- LEED ND: Built Project. Completed development projects.
LEED for Residential
This LEED certification can be applied to all types of residential projects.
- Single Family Homes. New single-family homes that are attached or detached.
- Multi Family Homes. Applicable to any predominantly multifamily building with two or more units and any number of stories.
- Multi Family Homes Core and Shell. New construction and major renovation multifamily projects that do not include a complete fit out
LEED for Cities and Communities
Cities
These are places with a governing body, and include cities, towns, counties and other local government jurisdictions. In this category, certification is typically initiated by the governing body.
Communities
This is defined as places, such as regions, districts, business improvement districts (BIDs), economic development zones, neighborhoods, campuses, universities and military installations; either in planning and designing phase, existing developments or redevelopments. In communities, certification is spearheaded by private sector planners or developers, corporates, quasi-government authorities, universities or non-governmental organizations.
What does the LEED certification measure?
LEED focuses on the following concepts:
- Integrative process
- Location and transportation
- Sustainable sites
- Water
- Energy
- Materials and resources
- Indoor environmental quality (IEQ)
LEED certification process
To establish LEED-certified buildings, projects are required to satisfy all prerequisites and earn a minimum number of points. Depending on the points collected, building projects may reach the following LEED certification levels:
- Certified: 40–49 points
- Silver: 50–59 points
- Gold: 60–79 points
- Platinum: 80+ points
Benefits of becoming LEED-certified
Becoming LEED-certified offers numerous benefits to building owners, occupants, and the environment. Here are some key advantages of achieving LEED certification:
- Improved Property Value – Green buildings and amenities command a rent premium, with lease-up rates averaging 20% more than non-green structures.
- High Building Performance – following the standards set by LEED enables building owners to incorporate environmentally sustainable design, development, management, and efficiency into their building.
- Occupant Health and Satisfaction– Occupants have increased productivity and well-being in buildings with improved air quality and other wellness features.
Earning LEED certification credits using uHoo Aura
uHoo Aura is the most comprehensive indoor environmental quality monitor that captures information about 13 factors that affect an indoor environment. These factors include temperature, humidity, CO2, TVOC, PM1, PM2.5, PM4, PM10, air pressure, formaldehyde, carbon monoxide, light, and noise. The device is also upgradable to measure two more parameters namely nitrogen dioxide and ozone or choose one among sulfur dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia, depending on your specific industry and/or requirements. Additionally, uHoo Aura comes with a dashboard that displays real-time status of the building’s IEQ.
LEED v4.1 Requirements supported by uHoo
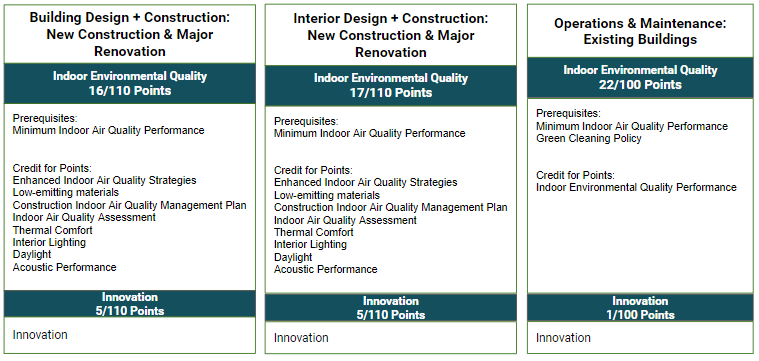
With the data from uHoo Aura, you can have the competence to know what’s in your indoor environment, come up with strategies to improve your IEQ, and make your building LEED-certified.


